Viewings: 5052
Basic information about the galaxies gathered in multiple directories. The first galactic directory was created in 1784 Charles Messier and P. Masinam. It includes 108 nebulae, which the authors nazvali motionless, not to be confused with comets moving. Objects included in the Messier catalogue, denoted by the letter M with a serial number. So, for example, M31 designation of the Andromeda nebula. Currently widely used "New General catalogue" Dreyer (its first part was published in 1888), it included about 13,000 objects. Galaxy M31 in the directory Dreyer designated NGC 224. In the late 60's. our century were created "Morphological catalog of galaxies" (group B. A. Vorontsov-Velyaminov) and "the Second bibliographic catalogue of bright galaxies" (group Gokudera). These directories contain tens of thousands of objects.
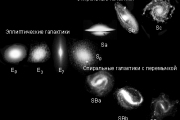
Galaxies differ from each other primarily in their appearance. In 1925, Hubble has offered morphological classification of galaxies, which in some modified form is used today. Put the following main classes of galaxies: elliptic E, lenticular SO, spiral S, spiral with a jumper'SV, wrong Ir.
Surface brightness galaxies gradually decreases from the center to the periphery of the law by the equation of an ellipse. The internal structure of the photographs of elliptical galaxies is not found, although many of them have small star-shaped nuclei.
Only the closest galaxies is possible to allocate separate stars. So typically the stellar content of galaxies determined from the analysis of total radiation of the stars. According to observations, elliptical galaxies contain only yellow and red stars in them are practically no gas and no young stars. The age of the stars in these systems, at least 5 to 7 billion years.
Spectral line E-galaxies is very wide because of the large dispersion of velocities (up to 200 km/s). Stars rotate around the center of the galaxy in different planes. Visible compression E-galaxies is due to the fact that not all the orbits of stars sustainable. Orbit plane which is parallel to the axis of rotation of the whole system unstable. When a small gravitational influence of nearby stars movement of the stars in this orbit, quickly changed: the ellipse becomes a straight segment, and a falling star at the center of the star system. As a whole E-galaxies rotate slowly, with more than flattened system rotate faster than spherical.
The specific parameters of the E-galaxies span a wide range: the radius of 5-10 PDA, mass 106 - mon, luminosity 106 - 1012LСолнца (Solnca = 2*1033 grams LСолнца = = 4*1033 erg/s).
The largest of E-galaxies allocate in a separate group of cD galaxies. In these galaxies have a compact star system, surrounded by giant thin shell of stars. The dimensions of the shell may be dozens or even hundreds of KPS.
Galaxy cD are rare. Our nearest and the most studied of them - system M 87. The radius of its Central components about 8 KPC, and the shell can be traced at a distance of up to 60 KPC from the center. The mass M 87 about mon. The largest of the known cD systems is the shell radius of about 2 IPC - galaxy A.
It turns out that the cD systems are always in the center of clusters of galaxies. Galaxy M 87 is the Central system in the cluster of galaxies in the constellation Virgo.
Mass determine various characteristics of galaxies has allowed to establish important empirical regularities. It turns out that the more luminosity E-galaxies LB, the greater the width of the lines in its spectrum. Width of lines is proportional to the velocity dispersion звездsu.
The relationship between LB иsu looks LB su4. This ratio is called the ratio of the Faber - Jackson, it can be used to measure distances in the Universe. It was also found that the giant elliptical galaxy more rich in metals than dwarf galaxies of this type. This difference is connected with the peculiarities of the process of star formation in massive and low-mass galaxies.
Some of the giant elliptical galaxies have a powerful radiation, sources of which are hot gas and stars. Along with a Central source of radio emission these galaxies have extended in size, sometimes hundreds PDA field of radio emission, often placed symmetrically in relation to the optical image of the galaxy. The intensity of radiation reaches 1012 LСолнца. The Central system of the cluster of galaxies in the constellation Perseus is the cD galaxy NGC 1275, about it is told in the next article in this Bulletin. One of the most interesting structural characteristics of radio galaxies are jets. The jets are a fine education. They start at the core of the galaxy and extend for hundreds of PDA to the border area of radio emission. Radiation has synchrotron nature: emit jets of relativistic electrons moving in a magnetic field. In the optical spectra of radio galaxies often see emission lines of ionized hydrogen. The emergence jets connected with the activity of nuclei of galaxies. The nature of this activity has not been determined.
In late 70-ies were detected in E-galaxies hot corona that glow in the x-ray range (temperature about 107). If gas crowns is in equilibrium in the gravitational field of the galaxy, mass crowns order mol. And, for example, the galaxy M 87 weight of the crown about mon, its size is about 200 PDA.
Types of galaxies
Galaxies are of various shapes and sizes. Astronomer Edwin Hubble was divided into four main groups: elliptic - E, spiral - S, linear-spiral - SB and wrong - I. he Then added the letters and numbers to indicate how splyusnuta elliptical galaxy or how tight sleeves spiral galaxies are adjacent to the kernel.
Class
S - Helical ( Spiral )
C - Compact ( Compact )
E - Elliptic ( Ellipticals )
I - Wrong ( Irregular )
D - Dwarf ( Dwarf )
L - Lenticular ( S0 )
P - Special ( Peculiar )
B - With a jumper ( Barred )
R - Ring ( Ring )
M - multiple
















