Viewings: 4387
In 1876, when it was known only about 150 asteroids, D. Kirkwood tried to understand "chaos" asteroid orbits and found about 10 groups of asteroids, each of which consisted of only 2-3 members moving on similar orbits. Among them were, for example, 3 Juno and 97 of the Clot.
It seemed that these groups can be seen as related by common descent, and that members of the groups - the wreckage of a larger phone Attempts Kirkwood continued F. Tisserant, formed in 1891 its list of 417 asteroids. The number of groups grew along with the growth of the number of open asteroids.
Essentially, this was the version of the hypothesis of Alberta, only the relationship does not extend to all the asteroids, and for some groups. But it was not so simple, and kinship groups questionable. This became clear when the Japanese astronomer K. Hirayama in 1918-1919 drew attention to the fact that the similarity of orbits of asteroids does not mean that these asteroids in the past were parts of the same, a larger body. When a large number of asteroids is not excluded join asteroids in the group due to the accidental similarity of their orbits. But the main mistake was the fact that in the search for "relatives" compared modern orbits of asteroids. Meanwhile perturbations by the planets, accumulate over time, could gradually beyond recognition and different change the orbits of those asteroids that was indeed the debris of the same body and really moved in the past on similar orbits. On the other hand, the similarity of the modern orbit does not mean that in the distant past asteroids moved on similar orbits. Therefore, using the methodology of Kirkwood, if you can find the real group "relatives", it is only recently formed, say, 1000 years ago.
Hirayama has raised the question: is it possible to identify groups of asteroids, related longtime relationship, i.e. a family of asteroids (as he called them), and how to do it?
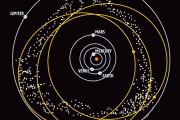
The theory of the motion of the satellites of the planets taking into account perturbations, developed earlier by Languages, pointed out that the eccentricities and inclinations of the orbits of satellites remain almost unchanged for large periods of time, while the longitude of the pericenter and node of the orbit are constantly changing. This led Hirayama to the idea "invariant" (unchanged) elements of the asteroid orbits, which also would not change (or changed slowly) under the action of planetary perturbations. Such elements can be used to search for a family of asteroids. Hirayama found such invariant elements and called their own orbital elements, i.e. inherited asteroids from their "parent". Of course, the crushing of asteroid fragments, having different about small additives to the orbital velocities are moving to different orbits with a slightly different elements. However, these differences are not large enough to prevent learn members of the family.
Generally speaking, own elements are keplerova elements of the orbits of asteroids, corrected for age-old resentment. The typical orbits own inclinations and eccentricities is almost not affected by age-old to change, and we can assume that they will remain unchanged for billions of years. As for the longitude of perihelion and longitude of the site, they are changing much faster. Own longitude of perihelion very slowly (at the rate from tens of seconds to tens of minutes of arc per year), but growing, while private node longitude decreases at the same rate. for bodies in the ring of asteroids orbital period of the perihelion and the ascending node of the orbit around the Sun of the order of several thousand years. They increase with the reduction of the sizes of the orbits.
Thus, asteroids long "remember" only the inclination and eccentricity, but quickly "forget" your site and perihelion.
Hirayama decided to use his own inclination and eccentricity orbits for searches families. First, in order to simplify the calculations, it takes into account only the perturbations from Jupiter, ignoring the weaker the influence of Saturn and other planets. He was able to identify three families (family Themis, EOS and Korondi, named after one of the members of families), and then four more, and less confident, another six. But soon Hirame became clear that take into account the effects of Saturn and other planets is still necessary. Saturn, for example, has had a noticeable effect on the asteroids with a small average daily traffic. By doing this, Hirayama came to the conclusion about the existence of the five families - Themis, EOS, Coronita, Maria and Flora. These families in 1923 he took dozens of known asteroids. They were supplemented with the asteroids, open later.
Most numerous were the family of Flora. D. Bauer, on the basis of the adjusted them perturbation theory, divided it into four separate collection I, II, III and IV.
To the 70-s it became clear that the "nepotism" widespread among asteroids : from 1697 numbered by this time asteroids 712 (or 42 %) were attributed to 37 families. They haven "remember" orbit its parent body. Similar was the situation in smaller asteroids Palomar-Leiden Ferris: 980 new asteroids 389 (40 %) entered into a particular family of already known or new.
The family finds itself as an area of high concentration points on the intrinsic elements of the orbits. The boundaries of the families are not always confident, and the assignment of an asteroid to one or another family sometimes remains doubtful. Moreover, when different researchers consider perturbations of planets with varying degrees of accuracy and selected members of the family, using slightly different criteria, they get slightly different results. However, these differences are not fundamental and do not allow to doubt the very existence of nepotism from asteroids. A Japanese researcher I. Kosai by the end of 70-ies among 2125 numbered asteroids about 3/4 attributed to 72 families. American researchers J.. Grade, K. Chapman and J.. Williams suggest that the number of families exceeds 100. However, we have to be careful not to be mistaken for a family of random point group. Long believed that there exists a family of Hungary (a=1,8 a.e. ) and token (a=2,4 a. e. ) on the orbits of the large dip (own inclination 20-25O). However, in reality this is just a random group of asteroids, isolated from the rest of the ring empty areas secular resonances. The asteroids are not linked by a common origin, the same as members of groups Hilda, Apollo, Amur or Aton. They only have a similar dynamic evolution of the orbits.
It is not clear whether there is a family of Pallas, or we are again, as in the case of Hungary and Fokea, dealing with a group of asteroids, isolated secular resonances.
Many families of tens and hundreds of well-known members. Assume that the actual number of the members of the families by one to two orders of magnitude higher.
In the late 60-ies astrophysicist Halon tried to reveal the ring of asteroids (more precisely, in the known families) sokolki of recent origin. For this, he highlighted the orbit, similar, not two, but four own members (not counting the semimajor axis), including self-longitude of perihelion and private longitude of the site. Collection of Flora I al'ven found 13 such asteroids (out of 23), and in the collections of Flora II, III and IV, he discovered two groups consisting of 20 and 28 of asteroids. Similar groups have been identified in other families. Al'ven called them the jet streams, or just jets, or threads.
How would closely neither were located nodes orbits in the formation of fragments after the crushing of the parent body of the family, due to the small differences in the sizes of the orbits of several hundred thousand years shards will still be distributed more or less evenly across all longitudes. Therefore, jet streams can be viewed as a young education, indicating recent crushings that occurred in the period of existence on the Earth. However, the Alven of a different opinion: he believes that the jet streams represent the structures of the bodies at ways to accumulate (unite).
Attempts to allocate streams made and other researchers. Using slightly different selection criteria, they received quite a controversial result: and threads, and their members were different. This gives rise to doubt as to the possibility of detection and the very existence of many of them.
Soviet astrophysicist Biuletyn showed that a significant part of families and jets contains only one rather large asteroid sharply distinguished among other smaller members of the family or of the jet. Of the 54 studied families and jets in 14 (26%) the largest member is superior to the other mass on the order and more. In four cases (7%) differences by mass are simply enormous - 1000 times or more. This means that the head of the family has a diameter more than in 10 times exceeds the diameter of the other asteroids. The heads of these families are Ceres and Vesta.
The occurrence of such family or a jet stream may be associated with the collision of asteroids, very different by weight, when a larger asteroid falling apart completely, and only loses in the form of fragments of a significant part of the mass, and with oblique, almost tangent collisions of asteroids with comparable masses. in the latter case, the formation of families with two large States. This collection is containing 19 Fortune and 21 Lutetia.
But most families formedaxis, apparently, in case of catastrophic destruction of asteroids, which gave rise to these families, and does not contain such asteroids giant.
Fragments formed by the splitting of the asteroid, because of the slightly different from them heliocentric speeds overtake each other, remaining in orbit around its parent body. For several years or tens of years, they are stretched along the orbit, forming Roy. It's funny that survived "parent" families do not tolerate their ' children". The parent asteroid scoop them out of the swarm, and because of the low relative speed (tens or hundreds of meters per second) meeting of the asteroid with his chip does not lead to further fragmentation: splinter just buries itself in the regolith their parents (under the regolith is understood surface layer of ground downs numerous small asteroid fragments). However, a fate befalls the very few. In addition, by the gravitational influence of parents cast their parts on the periphery of the arisen Roy, reducing the spatial density of bodies in PoE. A similar effect has on Roy and planetary perturbations.
However, with the formation of the families of the crushing of asteroids, things are not as easy as it may seem. When in 1982 the employees of the Institute of Technology in Pasadena (USA) Ddavis, Koeppen, Regenberg and Wagenseller specifically investigated the question of education of the family EOS, it appeared that the parent asteroid, the size of which exceeded apparently 180 km before you experience a catastrophic collision with a large object (which would have to form a family), had to face at least a dozen smaller phone Under the action of their shock parent asteroid was "collapse" into blocks with a characteristic size of about 10 km held alongside each other only by the forces of gravity. Meanwhile, remained an object of a diameter of 98 km (it myself EOS). We can assume that it is preserved 20 percent balance mass consisting of not scattered fragments. But then, as researchers believe, the next largest body would have to have a diameter of just 5 km. meanwhile, the second largest member of the family has a diameter of 80 km. Only through a series of very artificial assumptions are able to circumvent these difficulties.
















